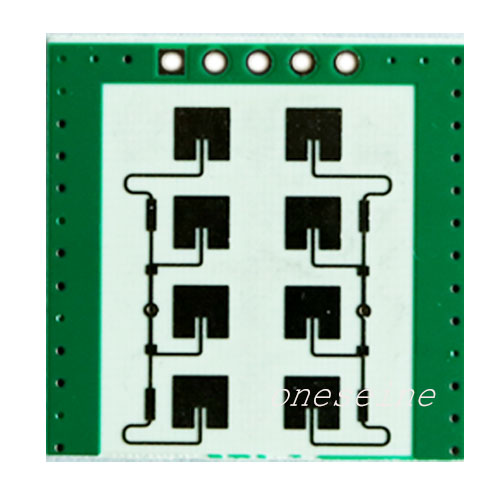
Microwave RF PCB
PCB Antenna vs. FPC Antenna RF PCB Printed Circuit Board Antenna Fabrication
- rogers circuit board
- rogers pcb material
- 2 layer
- sensor pcb
- Product description: Pcb printed antenna calculator PCB antenna design PCB antenna types PCB antenna Calculator PCB antenna radiation pattern 2.4ghz pcb antenna design
PCB Antenna vs. FPC Antenna RF PCB printed circuit board Antenna Fabrication
PCB description:
Layer:2
Cu Thk:1OZ
Minimum Hole Size:0.2mm
Impedance Control:50Ω
Base Material:Rogers
Material:Rogers 4003C
Solder Mask Color:Green
Minimum Trace Spacing:4mil
Choosing the Right Antenna for Your Wireless Device
When designing a wireless product like a Wi-Fi router, Bluetooth tracker, or IoT device, selecting the right antenna is crucial for optimal performance and cost. Two of the most common internal antenna types are PCB (Printed Circuit Board) antennas and FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit) antennas. Here's a breakdown of their key differences to help you decide.
What is a PCB Antenna?
A PCB antenna is a conductive trace etched directly onto the main rigid circuit board of the device. It is essentially a pattern of copper that forms the antenna.
Material: FR4 (standard rigid PCB material)
Structure: Rigid and fixed.
Integration: Built-in as part of the main PCB.
What is an FPC Antenna?
An FPC antenna is a separate, flexible antenna made from a thin film of polyimide or PET. It features a conductive trace and is attached to the main PCB via a connector (like an I-PEX connector) or solder.
Material: Flexible polyimide film.
Structure: Thin, lightweight, and bendable.
Integration: An external component that is connected to the main PCB.
When to Choose Which Antenna?
Choose a PCB Antenna if:
Cost is the primary driver (high-volume, low-cost consumer devices).
Your device has a simple, compact enclosure with little internal space.
The antenna location on the main board is free from significant electromagnetic interference.
You require high durability and a simple assembly process.
Choose an FPC Antenna if:
Performance is a top priority. You need to place the antenna in an ideal location for the best signal reception.
Your device has a complex or small enclosure where a rigid board doesn't fit well.
You need design flexibility for prototyping and iterative testing.
The main PCB is too crowded with components that would interfere with an integrated antenna.
Conclusion
The choice between a PCB and FPC antenna boils down to your project's specific needs for cost, performance, and mechanical design.
PCB Antennas offer the lowest cost and great simplicity for space-constrained, cost-sensitive designs.
FPC Antennas provide superior design flexibility and often better performance by allowing optimal placement, making them ideal for high-performance and compact wearable devices.
For your next wireless project, carefully consider your budget and enclosure design to select the best antenna type for reliable connectivity.
Categories
Latest News
Contact Us
Contact: Ms Tracy
Phone:
Tel:
Add: BludingA,Shixiaganglian Industrial Park,Shajing,Baoan,Shenzhen,China

 Tracy
Tracy