Printed Circuit Boards
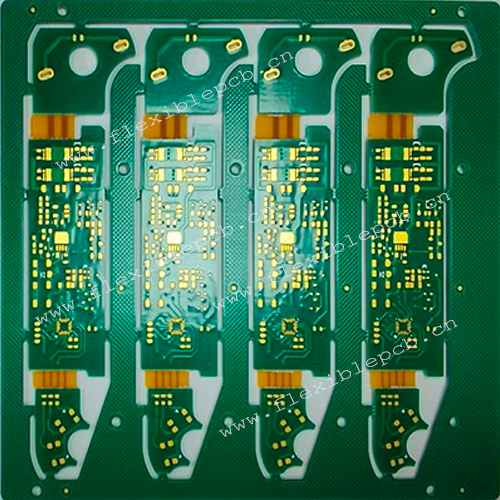
Six layer soft and hard combination board for Bluetooth earphones
- rigid flex pcb board
- flex circuit design
- flexible pcb factory near me
- flex circuit
- Product description: transparent flex pcb transparent flexible pcb transparent fpc mobile FPC 2 layer flex pcb stackup 4 layer flex pcb stackup 6 layer rigid-flex stackup flex pcb thickness würth rigid flex stacku
Six layer soft and hard combination board for Bluetooth earphones
Application field: Bluetooth earphones, wearable devices
Material: Rigid part: Shengyi s1000-2M
Soft part: Shengyi double-sided adhesive free rolling
Plate thickness: 1.6mm
Process capability: small pore size
1、 Introduction to FPC - What is FPC?
FPC: Full English spelling for Flexible Printed Circuit, which means flexible printed circuit board or flexible circuit board in Chinese, abbreviated as flexible board.
It is a conductive circuit pattern made by using optical imaging pattern transfer and etching techniques on a flexible substrate surface. The surface and inner layers of double-sided circuit boards and multi-layer circuit boards are electrically connected through metallized holes, and the surface of the circuit pattern is protected and insulated with PI and adhesive layers.
Flexible circuit boards are mainly divided into single sided flexible circuit boards, hollow flexible circuit boards, double-sided flexible circuit boards, multi-layer flexible circuit boards, and rigid flex PCBs
PCB: Full English Pinyin Printed Circuit Board, which means printed circuit board in Chinese, usually referring to rigid printed circuit board, abbreviated as hard board.
2、 Development Trends - Development History of FPC
The flexible circuit board industry first emerged in Japan around 2002. The flexible circuit board industry outside Japan began to sprout in 2003, rapidly expanded in 2005, and experienced a decline in 2006. In mid-2007, the flexible circuit board industry bottomed out and began to recover in 2008.
In 2005, the flexible circuit board industry had low barriers and high profits, attracting a large number of enterprises to enter.
In 2006, competition became increasingly fierce, and the phenomenon of oversupply was very serious. Many enterprises had to lower prices repeatedly in order to survive, even operating at a loss. At the same time, downstream customers of the softboard industry, such as large EMS manufacturers, have added softboard departments and no longer outsourced softboard business, which has made the softboard industry worse.
2007 was a turbulent year for the soft board industry. Firstly, there has been a significant decline in profits. M-FLEX, a manufacturer of flexible circuit boards, had a net profit of only $3 million in the 2007 fiscal year, compared to $40.4 million in the 2006 fiscal year, a 93% decrease in net profit. Similarly, another large circuit board factory, Jiatong Technology, which is listed in Hong Kong, lost $29.8 million in fiscal year 2007, while it made a profit of $12.4 million in fiscal year 2006. Secondly, there was a decrease in sales. Jialianyi, the largest flexible circuit board factory in Taiwan, had sales of 7.79 billion Taiwan dollars in 2004, followed by three consecutive years of decline. In 2007, sales were 6.541 billion Taiwan dollars. Once again, the gross profit margin has declined. In 2004, Jialianyi's gross profit margin was 29%, and in 2007 it dropped to 12%. Young Poong, the largest softboard company in South Korea, has spun off its softboard business from a listed company to prevent investors from looking too embarrassed. If the large factory still does so, the small factory will directly go bankrupt.
The massive closure of small factories has brought opportunities to the soft board industry, which has been recovering since early 2008. But the softboard industry is facing a new challenge, which is the economic downturn. At the beginning of 2008, the global economy experienced a downward trend, with high oil prices, the subprime crisis, and a surge in food prices. The global economy has entered a downward trajectory, especially in emerging countries. The decline in demand for soft boards stems from consumer electronics products. When the economy is in a downward trend, the first hit is the demand for consumer electronics products with non rigid demand, including mobile phones, laptops, tablet TVs, LCD displays, digital cameras, DVs, and other products.
3、 Characteristics of FPC Flexible Circuit Board
1. Small size and light weight. Can be used in precision small electronic equipment applications;
2. Can be bent or flexed. Can be used to install any geometric shape equipment body;
3. In addition to static bending, it can also be dynamically bent. Can be used for connecting dynamic electronic components;
4. Expanding into three-dimensional space, improving the freedom of circuit design and mechanical structure design, and fully utilizing the functions of printed boards;
5. Flexible boards, except for ordinary circuit boards. It can also have various functions, such as sensing coils, electromagnetic shielding, touch switch buttons, etc.
The difference between FPC and PCB: it has the characteristics of being short, lightweight, and foldable
4、 The main production raw materials for FPC flexible circuit boards
The main raw materials include: 1. substrate, 2. covering film, 3. reinforcement, and 4. other auxiliary materials.
1. Substrate
1.1 Adhesive substrate
The adhesive substrate mainly consists of three parts: copper foil, adhesive, and PI. There are two types of substrates: single-sided substrate and double-sided substrate. Materials with only one copper foil are single-sided substrates, while materials with two copper foils are double-sided substrates.
1.2 Adhesive free substrate
Non adhesive substrate refers to a substrate without an adhesive layer. Compared to ordinary adhesive substrate, it has fewer intermediate adhesive layers and only consists of copper foil and PI. Compared to adhesive substrate, it has thinner, better dimensional stability, higher heat resistance, higher bending resistance, and better chemical resistance, and is now widely used.
Copper foil: Currently, the commonly used copper foil thicknesses are as follows: 1OZ, 1/2OZ, 1/3OZ. Currently, thinner copper foils with a thickness of 1/4OZ are being introduced, but this material is already being used in China to produce ultra-fine line (line width and line spacing of 0.05mm and below) products. With increasing customer demands, materials of this specification will be widely used in the future.
2. Covering film
It mainly consists of three parts: release paper, adhesive, and PI. The only remaining parts on the product are adhesive and PI. The release paper will be torn off during the production process and will no longer be used (its function is to protect foreign objects on the adhesive).
3. Reinforcement
Used as a specific material for FPC, in a specific part of the product to increase support strength and compensate for the "soft" nature of FPC.
There are currently several commonly used reinforcement materials:
1) FR4 reinforcement: The main components are glass fiber cloth and epoxy resin adhesive, which are the same as the FR4 material used in PCB;
2) Steel reinforcement: composed of steel, with strong hardness and support strength;
3) PI reinforcement: Similar to the covering film, it consists of three parts: PI and adhesive release paper, but its PI layer is thicker and can be produced in a ratio from 2 MIL to 9 MIL.
Differences between FPC reinforcement material FR4 and PI
They are all made of hard materials, used to strengthen and facilitate the installation of soft board areas to carry component areas.
FR4 is a glass fiber epoxy resin composite reinforcement material with low water absorption, good durability, and good bending strength.
PI (polyimide) has a higher price, but its resistance is better.
4. Other auxiliary materials
1) Pure adhesive: This adhesive film is a thermosetting acrylic adhesive film composed of protective paper/release film and a layer of adhesive. It is mainly used for laminated boards, soft and hard bonding boards, and FR-4/steel sheet reinforcement boards to play a bonding role.
2) Electromagnetic protective film: pasted on the board surface to provide shielding effect.
3) Pure copper foil: only composed of copper foil, mainly used for hollow board production.
5、 Types of FPC flexible circuit boards
There are six types of FPC differentiation:
A. Single panel: Only one side has wiring.
B. Double sided board: Both sides have wiring.
C. Hollow board: also known as window board (finger facing window opening).
D. Layered board: Two sides of the circuit (separate).
E. Multi layer board: Two or more layers of circuit.
F. Soft hard combination board: A product that combines soft and hard boards.
6、 The Future of FPC Flexible Circuit Board
We need to continuously innovate from four aspects, mainly in:
1. Thickness: The thickness of FPC must be more flexible and thinner;
2. Bending resistance: Being able to bend is an inherent characteristic of FPC, and future FPC must have stronger bending resistance, exceeding 10000 times. Of course, this requires better substrates;
3. Price: At present, the price of FPC is much higher than that of PCB. If the price of FPC drops, the market will definitely be much wider.
4. Process level: In order to meet various requirements, the FPC process must be upgraded, and the minimum aperture, minimum line width/line spacing must meet higher requirements.
Categories
Latest News
Contact Us
Contact: Ms Tracy
Phone:
Tel:
Add: BludingA,Shixiaganglian Industrial Park,Shajing,Baoan,Shenzhen,China


 Tracy
Tracy